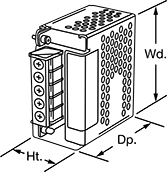
DIN-Rail Power Supplies
Mount these power supplies onto DIN rails inside electrical panels and enclosures—they convert AC to DC voltage to power electronic equipment. With a set of standard features, they're a cost-effective option for clean, controlled environments with a stable supply of electricity. Use them to power testing and measuring devices as well as commercial equipment, such as printers and ATMs. Unlike heavy duty power supplies, they're not made for tough, dirty environments.
All of these power supplies use switching regulation, which means they produce the stated voltage despite fluctuations in your input power and the power being drawn by your system, and they won’t become too hot.
If you exceed the maximum voltage, current, or load, these power supplies shut down to protect both the power supply and the connected equipment.
With various domestic and international certifications, such as UL listing, CE marking, and TUV certification, these power supplies meet stringent safety standards. Power supplies with an NEC Class 2 or LPS output limit the risk of electrical shock should something fail inside the power supply. Power supplies with an IP20 rating prevent your fingers from touching internal components and accidentally shocking yourself.
Maximum output noise is also known as ripple noise. The lower the value, the less interference the power supply creates. For most applications, a value over 100mVpp isn’t a problem. However, when using to power extremely sensitive electronics, such as audio equipment and high-precision measuring and testing equipment, you’ll want an output noise around 5mVpp or less.
Power factor shows how effectively a power supply draws AC power from the main electrical supply. The higher the power factor—up to a maximum score of 1—the lower your operating cost.
Efficiency describes how good a power supply is at converting the AC power it draws from your main electrical supply into DC power. High-efficiency power supplies cost less money to operate and produce less heat, meaning cooler temperatures in your electrical cabinet.
Power supplies with an output voltage signal send a signal that indicates the status of their output voltage, so you know if your power supply isn't working correctly. Configure them to light up a panel or activate an alarm when voltage drops, or connect them to a PLC for remote system monitoring.
Power supplies that cannot be sold to the regions listed do not meet local energy efficiency requirements.
Output | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Adjustment Range) | Current, A | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Efficiency | Low-Voltage Output Type | Environmental Rating | Specifications Met | Each | |
Single Phase—100-240V AC Input Voltage | ||||||||
Screw-Clamp Terminals Input and Output—With Output Voltage Signal | ||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5-16.5V DC) | 1.3 | 120 | 81% @ 230 V AC | NEC Class 2, LPS | IP20 | UL Listed C-UL Listed UL Recognized Component CE Marked TUV Rheinland Certified UL 508 | 00000000 | 000000 |
Compact Motor-Starting DIN-Rail Power Supplies

Sized to fit into small and cramped enclosures, these compact power supplies mount onto DIN rails to convert AC to DC voltage. Despite their size, they're designed to power motors, solenoid valves, and other devices that require large start-up current. To do so, they briefly boost power above their maximum output current. This means you don't have to use an oversized power supply just to handle occasional spikes in demand.
All of these power supplies use switching regulation, which means they produce the stated voltage despite fluctuations in your input power and the power being drawn by your system, and they won’t become too hot.
If you exceed the maximum voltage, current, or load, these power supplies shut down to protect both the power supply and the connected equipment. They also meet the voltage requirements for use in an SELV (separated extra low voltage) circuit.
Rated IP20, these power supplies prevent your fingers from touching internal components and accidentally shocking yourself. They're UL and C-UL certified and CE marked so you know they meet stringent safety standards. With Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C, and D environmental ratings, all are safe for use in environments that are not normally hazardous, but where concentrations of combustible gases may occur infrequently.
Maximum output noise is also known as ripple noise. The lower the value, the less interference the power supply creates. For most applications, a value over 100mVpp isn’t a problem. However, when using to power extremely sensitive electronics, such as audio equipment and high-precision measuring and testing equipment, you’ll want an output noise around 5mVpp or less.
Efficiency describes how good a power supply is at converting the AC power it draws from your main electrical supply into DC power. High-efficiency power supplies cost less money to operate and produce less heat, meaning cooler temperatures in your electrical cabinet.
Power supplies cannot be sold to California or Vermont due to energy efficiency requirements.
Output | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Adjustment Range) | Current, A | Peak Current | Power, W | No. of Power Connections | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Efficiency | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Cannot Be Sold To | Each | |
Single Phase—100-240V AC Input Voltage | ||||||||||||
Screw-Clamp Terminals Input and Output | ||||||||||||
| 15V DC (12-15V DC) | 3.4 | 5.1 A, continuous | 50 | 2 | 50 | 86% @ 230 V AC | 2.95" | 1.77" | 3.8" | CA, VT | 0000000 | 0000000 |
Low-Profile DIN-Rail Power Supplies

Less than 2 1/2" deep, mount these power supplies to a DIN rail in shallow enclosures and control panels, such as those used in building automation systems. They briefly boost power above their maximum operating current to start motors, actuate solenoid valves, and other applications that require a higher starting current than their operating current. All of this means you get a more powerful power supply in a compact size.
These power supplies use switching regulation, which means they produce the stated voltage despite fluctuations in your input power and the power being drawn by your system, and they won’t become too hot.
If your power supply exceeds the maximum voltage or load, these power supplies protect both the power supply and the connected equipment. Some also protect against excessive temperatures. All meet the voltage requirements for use in a SELV (separated extra low voltage) circuit.
Rated IP20, these power supplies prevent your fingers from touching internal components and accidentally shocking yourself. They have also passed strict U.S., Canadian, and European Union safety standards.
Maximum output noise is also known as ripple noise. The lower the value, the less interference the power supply creates. For most applications, a value over 100mVpp isn’t a problem. However, when using to power extremely sensitive electronics, such as audio equipment and high-precision measuring and testing equipment, you’ll want an output noise around 5mVpp or less.
Efficiency describes how good a power supply is at converting the AC power it draws from your main electrical supply into DC power. High-efficiency power supplies cost less money to operate and produce less heat, meaning cooler temperatures in your electrical cabinet.
Output | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Adjustment Range) | Current, A | Peak Current | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Efficiency | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Protections Provided | Each | |
Single Phase—90-240V AC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
Screw-Clamp Terminals Input and Output | |||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5-16.5V DC) | 1 | 1.2 A, 3 seconds | 15 | 120 | 85% @ 230 V AC | 3.5" | 0.7" | 2.3" | Overload, Overvoltage | 0000000 | 000000 |
| 15V DC (13.5-16.5V DC) | 2 | 2.4 A, 3 seconds | 30 | 120 | 89% @ 230 V AC | 3.5" | 1.4" | 2.3" | Overload, Overvoltage | 0000000 | 00000 |
| 15V DC (13.5-16.5V DC) | 4 | 4.8 A, 3 seconds | 60 | 120 | 89% @ 230 V AC | 3.5" | 2" | 2.3" | Overload, Overvoltage | 0000000 | 00000 |
| 15V DC (13.5-16.5V DC) | 6.13 | 7.3 A, 3 seconds | 92 | 120 | 89% @ 230 V AC | 3.5" | 2.8" | 2.3" | Overload, Overvoltage, Over Temperature | 0000000 | 00000 |
Multiple-Voltage DIN-Rail Power Supplies

Power multiple devices with different voltages at the same time. These power supplies convert AC to DC voltage or step down high DC voltages to low DC voltages. Mount them to the DIN rails inside industrial cabinets and electrical panels, or unscrew the DIN clips to mount to any flat surface.
All of these power supplies use switching regulation, which means they produce the stated voltage despite fluctuations in your input power and the power being drawn by your system, and they won’t become too hot.
If you exceed the maximum temperature or load, these power supplies shut down to protect both the power supply and the connected equipment.
Rated IP20, they are designed to stop your fingers from touching internal components, which prevents accidental shocks. With various certifications, such as CE Marked, UL recognized, and C-UL recognized, these power supplies meet stringent safety standards. They have been safety tested for both AC and DC voltage inputs. They also meet specifications for UL 94 V-0, so they will self-extinguish within ten seconds if they catch fire, and won’t cause additional fires by dripping.
Maximum output noise is also known as ripple noise. The lower the value, the less interference the power supply creates. For most applications, a value over 100mVpp isn’t a problem. However, when using to power extremely sensitive electronics, such as audio equipment and high-precision measuring and testing equipment, you’ll want an output noise around 5mVpp or less.
Power factor shows how effectively a power supply draws AC power from the main electrical supply. The higher the power factor—up to a maximum score of 1—the lower your operating cost.
Efficiency describes how good a power supply is at converting the AC power it draws from your main electrical supply into DC power. High-efficiency power supplies cost less money to operate and produce less heat, meaning cooler temperatures in your electrical cabinet.
Output | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Output Power Connections | Voltage (Current) | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Power, W | Power Factor | Efficiency | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Specifications Met | Each | |
Single Phase—100-240V AC/100-353V DC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
Screw-Clamp Terminals Input and Output | |||||||||||
| 2 | 15V DC (1 A) -15V DC (1 A) | 300 300 | 30 | 0.59 @ 120 V AC 0.46 @ 240 V AC | 68% @ 120 V AC 68% @ 240 V AC 68% @ 110 V DC | 4.7" | 2.6" | 1.3" | UL Recognized Component C-UL Recognized Component UL 94 V-0 | 0000000 | 0000000 |
| 3 | 5V DC (3 A) 15V DC (0.5 A) -15V DC (0.5 A) | 100 300 300 | 30 | 0.56 @ 120 V AC 0.44 @ 240 V AC | 68% @ 120 V AC 68% @ 240 V AC 68% @ 110 V DC | 4.7" | 2.6" | 1.3" | UL Recognized Component C-UL Recognized Component CE Marked UL 94 V-0 | 0000000 | 000000 |
Power Supplies

(Screw Terminal Input ×
Screw Terminal Output)
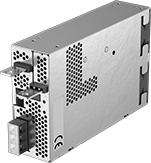
To power electronics ranging from simple prototypes to complex industrial automation and process control equipment, these general purpose power supplies convert AC to DC voltage. Mount them to a surface inside your device’s enclosure.
So you don’t accidentally touch internal components and shock yourself, these power supplies have their own housing. If you occasionally need to poke around inside your device’s enclosure, the housing also protects the power supplies themselves from damage. But compared to open-frame power supplies, these have a larger footprint, so they won’t fit in tight spaces.
For output wire connections, choose from standard screw terminals, screw-clamp terminals, and tab terminals. Use tab terminals if you have wires with ring terminal ends. To connect them, slide a screw through the hole in the tab terminal, slip the ring terminal from your wire over the screw, and tighten a nut on the end of the screw to hold everything in place. Screws, nuts, and ring terminals are not included.
All of these power supplies use switching regulation, which means they produce the stated voltage despite fluctuations in your input power and the power being drawn by your system, and they won’t become too hot. Power supplies that are SEMI F47 compliant meet standards for maintaining output voltage when input voltage dips. This is commonly known as voltage sag immunity.
If you exceed the maximum current, load, or voltage, these power supplies shut down to protect both the power supply and the connected equipment. All meet stringent safety standards.
Maximum output noise is also known as ripple noise. The lower the value, the less interference the power supply creates. For most applications, a value over 100mVpp isn’t a problem. However, when using to power extremely sensitive electronics, such as audio equipment and high-precision measuring and testing equipment, you’ll want an output noise around 5mVpp or less.
Power factor shows how effectively a power supply draws AC power from the main electrical supply. The higher the power factor—up to a maximum score of 1—the lower your operating cost.
Efficiency describes how good a power supply is at converting the AC power it draws from your main electrical supply into DC power. High-efficiency power supplies cost less money to operate and produce less heat, meaning cooler temperatures in your electrical cabinet.
Power supplies that cannot be sold to the regions listed are restricted by local energy efficiency requirements.
For technical drawings and 3-D models, click on a part number.
Output | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Voltage Adjustment) | Current, A | Power, W | Number of Power Connections | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Power Factor | Efficiency | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Protections Provided | Specifications Met | Cannot Be Sold To | Each | |
Single Phase—100V AC-240V AC Input Voltage | ||||||||||||||
Screw Terminals Input × Screw Terminals Output | ||||||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 1 | 15 | 1 | 150 | Not Rated | 77% @ 100 V AC 78.5% @ 115 V AC 79.5% @ 230 V AC | 1.5" | 3.2" | 2.9" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant, TUV Rheinland Certified | CA, VT | 00000000 | 000000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 2 | 30 | 1 | 150 | Not Rated | 81% @ 100 V AC 81.5% @ 115 V AC 82% @ 230 V AC | 1.5" | 3.2" | 3.5" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant, TUV Rheinland Certified | CA, VT | 00000000 | 00000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 3.5 | 52.5 | 1 | 150 | 0.87 @ 230 V AC, 0.98 @ 100 V AC, 0.98 @ 115 V AC | 80% @ 100 V AC 80.5% @ 115 V AC 82% @ 230 V AC | 1.5" | 3.2" | 3.9" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant, TUV Rheinland Certified | CA, VT | 00000000 | 00000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 6.7 | 100.5 | 1 | 150 | 0.9 @ 230 V AC, 0.98 @ 100 V AC, 0.98 @ 115 V AC | 83% @ 100 V AC 83% @ 115 V AC 86% @ 230 V AC | 1.6" | 3.8" | 4.3" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, D Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant | CA, VT | 00000000 | 00000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 10 | 150 | 1 | 150 | 0.93 @ 230 V AC, 0.98 @ 100 V AC, 0.98 @ 115 V AC | 84% @ 100 V AC 84% @ 115 V AC 87% @ 230 V AC | 1.6" | 3.8" | 5.1" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, D Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant | CA, VT | 00000000 | 00000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 20 | 300 | 2 | 150 | 0.95 @ 230 V AC, 0.98 @ 115 V AC, 0.99 @ 100 V AC | 81% @ 100 V AC 82% @ 115 V AC 84% @ 230 V AC | 1.6" | 4" | 7.5" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, D Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant | __ | 00000000 | 000000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 40 | 600 | 2 | 150 | 0.95 @ 230 V AC, 0.98 @ 115 V AC, 0.99 @ 100 V AC | 82% @ 100 V AC 82% @ 115 V AC 85% @ 230 V AC | 2.4" | 4.7" | 7.5" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, D Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant | __ | 00000000 | 000000 |
Screw Terminals Input × Tab Terminals Output | ||||||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 67 | 1,005 | 1 | 210 | 0.95 @ 230 V AC, 0.98 @ 100 V AC, 0.98 @ 115 V AC | 82% @ 100 V AC 82% @ 115 V AC 85% @ 230 V AC | 2.4" | 5.9" | 9.5" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, D Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant | __ | 00000000 | 000000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 100 | 1,500 | 1 | 210 | 0.95 @ 230 V AC, 0.98 @ 100 V AC, 0.98 @ 115 V AC | 82% @ 100 V AC 82% @ 115 V AC 85% @ 230 V AC | 2.4" | 7" | 10.6" | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | UL Recognized Component, C-UL Recognized Component, CE Marked, D Marked, SEMI F47 Compliant | __ | 00000000 | 000000 |
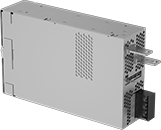
Remote On/Off Power Supplies
Save power by switching these power supplies on and off remotely, so devices only run when they're needed. Use them to convert AC voltage to DC to power electronic equipment ranging from simple prototypes to complex industrial automation and process control equipment. Mount them to a surface inside your device’s enclosure.
Besides turning them on and off, these power supplies have two other remote capabilities. Remote voltage sensing lets them compensate for any voltage that’s lost as it travels across the wires, ensuring that devices get the correct voltage. They also send a signal if the voltage drops, the cooling fan fails, or they exceed the maximum current, load, voltage, or temperature.
To use the remote features of these power supplies, you’ll need a wire connector (sold separately). Eight pin connectors enable remote on/off, voltage sensing, and signaling functionality using the power supply’s auxiliary power output. Ten pin connectors only add remote on/off and voltage sensing functionality. They require an external power source, such as a battery or another power supply.
So you don’t accidentally touch internal components and shock yourself, these power supplies have their own housing. They're good to use in spots where you occasionally need to access the inside of your device’s enclosure, since the housing also protects the power supplies themselves.
For output wire connections, they have either standard screw terminals or tab terminals. Choose tab terminals if you have wires with ring terminal ends. To connect them, slide a screw through the hole in the tab terminal, slip the ring terminal from your wire over the screw, and tighten a nut on the end of the screw to hold everything in place. Screws, nuts, and ring terminals are not included.
All of these power supplies use switching regulation, which means they produce the stated voltage despite fluctuations in your input power and the power being drawn by your system, and they won’t become too hot. In addition to sending a signal, if you exceed the maximum current, load, voltage, or temperature, these power supplies shut down to protect both the power supply and the connected equipment.
They're UL and C-UL Recognized Components, TUV Rheinland Certified, and CE Marked so you know they meet stringent safety standards.
Maximum output noise is also known as ripple noise. The lower the value, the less interference the power supply creates. For most applications, a value over 100mVpp isn’t a problem. However, when using to power extremely sensitive electronics, such as audio equipment and high-precision measuring and testing equipment, you’ll want an output noise around 5mVpp or less.
Power factor shows how effectively a power supply draws AC power from the main electrical supply. The higher the power factor—up to a maximum score of 1—the lower your operating cost.
Efficiency describes how good a power supply is at converting the AC power it draws from your main electrical supply into DC power. High-efficiency power supplies cost less money to operate and produce less heat, meaning cooler temperatures in your electrical cabinet.

Output | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Adjustment Range) | Current, A | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Power Factor | Efficiency | Wire Connector Required | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Each | |
Single Phase—100V AC-240V AC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
Screw Terminal Input × Screw Terminal Output | |||||||||||
| 15V DC (10.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 22 | 330 | 150 | 0.98 @ 100 V AC 0.95 @ 200 V AC | 78% @ 100 V AC 81% @ 200 V AC | 8 Pin, 10 Pin | 1.65" | 4.02" | 6.69" | 0000000 | 0000000 |
| 15V DC (10.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 43 | 645 | 150 | 0.98 @ 100 V AC 0.95 @ 200 V AC | 79% @ 100 V AC 82% @ 200 V AC | 8 Pin, 10 Pin | 2.4" | 4.72" | 7.48" | 0000000 | 000000 |
Screw Terminal Input × Tab Terminal Output | |||||||||||
| 15V DC (10.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 70 | 1,050 | 150 | 0.98 @ 100 V AC 0.95 @ 200 V AC | 82% @ 100 V AC 84% @ 200 V AC | 8 Pin, 10 Pin | 2.4" | 5.91" | 9.45" | 0000000 | 000000 |
| 15V DC (10.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 100 | 1,500 | 150 | 0.98 @ 100 V AC 0.95 @ 200 V AC | 83% @ 100 V AC 86% @ 200 V AC | 8 Pin, 10 Pin | 2.4" | 7.01" | 10.55" | 0000000 | 00000000 |
DIN-Rail DC to DC Converters
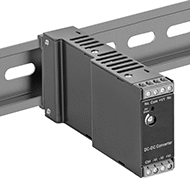
Mount these DC converters to DIN rails on fixtures such as industrial cabinets and electrical panels. By converting voltages, they let you connect power supplies to equipment that requires a different input voltage. They’re often used to power sensors or other components that require a lower voltage than surrounding equipment. Since they send a stable, consistent voltage to equipment, they can also be used to correct power supplies that send uneven voltages. All meet U.S. and Canadian, or European Union, safety standards.
If you exceed current limits, these converters will shut down to protect your equipment. Some converters have overvoltage or overload protection, as well.
The lower a converter’s maximum output noise, also known as ripple noise, the less electronic interference it creates. These converters will work in most applications.
For technical drawings and 3-D models, click on a part number.
Output | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Adjustment Range) | Current, A | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Mounting Fasteners Included | Specifications Met | Protections Provided | Each | |
Single Phase—9.5V DC-36V DC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 2.6 | 40 | 75 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 0000000 |
Single Phase—18V DC-36V DC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 4 | 60 | 100 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 000000 |
Single Phase—18V DC-75V DC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 2.6 | 40 | 75 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 000000 |
Single Phase—36V DC-75V DC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 4 | 60 | 100 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 000000 |
Output | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Current, A | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Mounting Fasteners Included | Specifications Met | Protections Provided | Each | |
Single Phase—9.5V DC-36V DC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
| -15V DC, 15V DC | 1.3 | 40 | 150 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 0000000 |
Single Phase—18V DC-75V DC Input Voltage | |||||||||||
| -15V DC, 15V DC | 1.3 | 40 | 150 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 000000 |
Output | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Current) | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Mounting Fasteners Included | Specifications Met | Protections Provided | Each | |
Single Phase—9.5V DC-18V DC Input Voltage | ||||||||||
| 5V DC (6A) 15V DC (0.3A) -15V DC (-0.3A) | 40 | 50 75 75 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 0000000 | 0000000 |
Single Phase—18V DC-36V DC Input Voltage | ||||||||||
| 5V DC (6A) 15V DC (0.3A) -15V DC (-0.3A) | 40 | 50 75 75 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 000000 |
Single Phase—36V DC-75V DC Input Voltage | ||||||||||
| 5V DC (6A) 15V DC (0.3A) -15V DC (-0.3A) | 40 | 50 75 75 | 2.3" | 1" | 4.9" | No | CE Marked | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 000000 |
DC to DC Converters
When your power supply sends out DC power at a higher voltage than you need, change to the proper voltage with these converters. They’re often used when a specific component, such as a sensor, requires a lower voltage than surrounding equipment. Use them to correct power supplies that send uneven voltages, too—they provide electricity at a stable, consistent voltage. They mount on flat surfaces, and are commonly fastened inside enclosures.
If you exceed the current limit, these converters will shut down to protect your equipment. Some converters have overvoltage protection, so they’ll do the same if you exceed voltage limits.
The lower a converter’s maximum output noise, also known as ripple noise, the less electronic interference it creates. These converters will work in most applications.
For technical drawings and 3-D models, click on a part number.
Output | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (Adjustment Range) | Current, A | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Mounting Fasteners Included | Protections Provided | Each | |
Single Phase–9V DC-36V DC Input Voltage | ||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 1 | 15 | 150 | 3.7" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent | 00000000 | 000000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 2 | 30 | 150 | 4.6" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 0000000 | 00000 |
Single Phase–18V DC-76V DC Input Voltage | ||||||||||
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 1 | 15 | 150 | 3.7" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent | 00000000 | 00000 |
| 15V DC (13.5V DC-16.5V DC) | 2 | 30 | 150 | 4.6" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 00000 |
Output | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Current, A | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Ht. | Wd. | Dp. | Mounting Fasteners Included | Protections Provided | Each | |
Single Phase–9V DC-36V DC Input Voltage | ||||||||||
| -15V DC, 15V DC | 0.5 | 15 | 150 | 3.7" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent | 00000000 | 000000 |
| -15V DC, 15V DC | 1 | 30 | 150 | 4.6" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 00000 |
Single Phase–18V DC-76V DC Input Voltage | ||||||||||
| -15V DC, 15V DC | 0.5 | 15 | 150 | 3.7" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent | 00000000 | 00000 |
| -15V DC, 15V DC | 1 | 30 | 150 | 4.6" | 2.1" | 1.1" | No | Overcurrent, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 00000 |
EMI Filtering IEC Connectors with Integrated Power Supply


Change AC voltage to DC voltage and bring power to electronic devices while protecting them from harmful electromagnetic interference (EMI). Even with their built-in power supply, these connectors have the same overall footprint as those without a power supply. All are for use with standard IEC power cords. Commonly used to convey power from wall outlets, you won’t have to wire your devices to an external power source. Instead, wire these connectors into your device with the terminals on the back of each connector.
For fast wire connections, these connectors have quick-disconnect terminals. The terminals slide together with the quick-disconnect terminals on your wiring and are easily disconnected by hand, but still provide a strong hold.
All of these connectors use switching regulation, which means they produce the stated voltage despite fluctuations in your input power and the power being drawn by your system, and they won’t become too hot. If you exceed the maximum voltage or load, the connectors will shut down to protect both the power supply and the connected device. They also meet the voltage requirements for use in a SELV (separated extra low voltage) circuit.
These connectors meet U.S. and international standards for safety. They also meet UL 94 V-0, which means they self-extinguish within 10 seconds if they catch fire, and won’t spread the fire by dripping. All have Class I shock protection—they're insulated and have a protective ground to prevent electrical shocks.
Maximum output noise is also known as ripple noise. When power supplies convert AC voltage to DC voltage, some noise from the AC voltage will carry into the output. While this noise won't affect most applications, it can interfere with other signals in extremely sensitive audio equipment and high-precision measuring and testing equipment. The lower the output noise, the less interference it creates.
Power factor and efficiency give you a sense for how efficiently these connectors draw AC power and convert it into DC power, which ultimately affects your operating cost. The closer the power factor is to 1, and the higher the efficiency percentage, the lower the operating cost. The more efficient the power supply, the cooler it runs.
For technical drawings and 3-D models, click on a part number.
Output | For Panel Cutout | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEC Style | Voltage | Current, A | Power, W | Max. Output Noise Peak-to-Peak, mV DC | Power Factor | Efficiency | Ht. | Wd. | Temp. Range, °F | Protections Provided | Each | |
Screw-On Male Receptacles | ||||||||||||
Single Phase—100V AC-240V AC Input Voltage | ||||||||||||
| C14 | 15V DC | 0.333 | 5 | 60 | 0.6 @ 115 V AC, 0.45 @ 230 V AC | 81% @ 230 V AC | 0.9" | 1.2" | -10° to 140° | Overcurrent, Overload, Overvoltage | 00000000 | 000000 |



























