How to Choose an Immersion Heater
Immersion heaters are the quickest and most efficient way to heat water, oil, coolant, and chemical solutions through direct contact. To choose an immersion heater that will work with your liquid, there are a few things to consider.
Determining the Watts You Need for an Immersion Heater
This chart shows the minimum watts needed to heat a container of room-temperature liquid with a six-hour warm-up time. Thick liquids, low initial temperatures, and shallow, uninsulated containers increase warm-up time and watt requirements. The watt requirements shown for chemical solutions were calculated for solutions with up to a 6% chemical concentration.
| Heat to 100°F | Heat to 130°F | Heat to 150°F | Heat to 170°F | Heat to 190°F | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallons | Water | Oil & Coolant | Chemical Solutions | Water | Oil & Coolant | Chemical Solutions | Water | Oil & Coolant | Chemical Solutions | Water | Oil & Coolant | Chemical Solutions | Water | Oil & Coolant | Chemical Solutions |
| 5 | 60 | 20 | 50 | 130 | 50 | 100 | 170 | 70 | 130 | 220 | 90 | 170 | 260 | 110 | 200 |
| 10 | 130 | 50 | 100 | 260 | 110 | 200 | 350 | 150 | 270 | 440 | 190 | 320 | 530 | 220 | 400 |
| 15 | 200 | 80 | 150 | 400 | 170 | 300 | 530 | 220 | 400 | 670 | 290 | 500 | 800 | 340 | 600 |
| 25 | 330 | 140 | 250 | 670 | 290 | 500 | 890 | 380 | 670 | 1,100 | 480 | 840 | 1,300 | 580 | 1,000 |
| 50 | 670 | 290 | 500 | 1,300 | 580 | 1,000 | 1,800 | 780 | 1,300 | 2,200 | 970 | 1,700 | 2,700 | 1,200 | 2,000 |
| 100 | 1,300 | 580 | 1,000 | 2,700 | 1,200 | 2,000 | 3,600 | 1,600 | 2,700 | 4,500 | 1,900 | 3,400 | 5,400 | 2,300 | 4,000 |
| 200 | 2,700 | 1,200 | 2,000 | 5,400 | 2,300 | 4,000 | 7,200 | 3,100 | 5,400 | 9,000 | 3,900 | 6,700 | 10,800 | 4,700 | 8,100 |
| 300 | 4,000 | 1,700 | 3,000 | 8,000 | 3,500 | 6,100 | 10,800 | 4,700 | 8,100 | 13,400 | 5,800 | 10,100 | 16,100 | 7,000 | 12,100 |
| 400 | 5,400 | 2,300 | 4,000 | 10,800 | 4,700 | 8,100 | 14,300 | 6,200 | 10,800 | 17,900 | 7,800 | 13,400 | 21,500 | 9,300 | 16,100 |
| 500 | 6,700 | 2,900 | 5,000 | 13,400 | 5,800 | 10,100 | 17,900 | 7,800 | 13,400 | 22,400 | 9,700 | 16,800 | 26,900 | 11,600 | 20,200 |
Choosing the Right Watt Density for an Immersion Heater
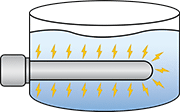
Watt density is the amount of power (in watts) an immersion heater produces per square inch of its surface area. One of the main causes of immersion heater failure is using a watt density that’s too high, so it’s critical to choose the lowest watt density possible. As long as you’re using enough watts to heat your liquid, the watt density can never be too low.
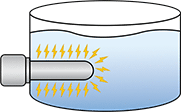
distributes power, the heat energy is
closely concentrated over a small surface area.
| Liquid | Maximum Watt Density
(Watts/Sq. In) |
|---|---|
| Clean Water | 100 |
| Oil and Coolant | 25 |
| Chemical Solution with
up to 6% Concentration |
35 |
Exceeding the maximum recommend watt density can damage the heating element and shorten the immersion heater’s service life. With water, a high watt density causes rapid scale and mineral deposit buildup on the heating element. With oil and coolant, it creates hot spots and overheats the heating element until it burns out. And with chemical solutions, it speeds up corrosion and quickly degrades the heating element.
Even at a low watt density, sludge, scale, and mineral deposits will still build up on the heating element. To remove buildup and extend the immersion heater’s service life, frequently clean the heating element with a scraper or a wire brush.
Choose from our selection of immersion heaters. In stock and ready to ship.
